What does the core update include and what are the consequences?
Google announced two new updates this week: the “March 2024 Core Update” and the “March 2024 Spam Update“. Unlike usual, the core update will take four weeks and lead to greater fluctuations in the search results. In any case, it already promises to be a particularly significant update.
The new Google Core Update will be one of the most important in recent years and is seen as a response to widespread criticism from SEO circles.
Does this mean that anyone who has worked with ChatGPT now has to worry about their ranking?
In particular, the update aims to penalize low-quality texts (created by AI?). Google aims to achieve a 40% reduction in “low-quality, unoriginal content” in search results.
However, not every text created with the help of AI is automatically spam. Google defines spam as follows:
Our long-standing spam policy states that the use of automation, including generative AI, is considered spam if the primary purpose is to manipulate ranking in search results.
However, the question remains as to how Google intends to recognize this purpose.
Talk to one of our experts and find out what consequences the update has for you and whether you should act now.
The update identifies three main sources of error:
The misuse of expired domains
This is unlikely to affect many of us. The misuse of expired domains is not a random occurrence, but a planned tactic in which the reputation of an old website is used to successfully place somebody’s own, often dubious or questionable content. Here, inferior products are supposed to benefit from the good reputation of the old domain. The search intentions for the old domain often differ from those for the new content.
The use of an old domain name for its product and to increase added value remains permitted.
Misuse of scaled content
Now it’s getting exciting. This is a further development of Google’s existing spam policy. With the core update, Google wants to take action against the mass creation of content with little content.
What does scaled content mean?
Scaled content is content that serves solely to manipulate search results without offering any real added value for users. This often involves a large amount of content that offers little or no benefit.
According to Google, it is irrelevant whether this content was created by automation, human labor or a combination of both.
Abuse of website reputation
The third change concerns the misuse of website reputation. All those who use so-called Parasite SEO for themselves should beware of this: These are sites, such as advertising sites or partner sites, which are “independent of the main purpose of the host site (…) and offer users little to no value.”
According to Google, the updates will not come into effect until May 5. It is likely that this is a clever move, because what would be more effective than patterns being revealed directly by the main players themselves?
Does it affect any type of automated content?
The distribution of content-free texts has become increasingly important since the end of 2022, particularly due to the rapid spread of AI tools such as ChatGPT and Aleph Alpha. The update should therefore mainly target this type of text.
Conversely, does this also mean that all texts that are created automatically are marked as spam?
Let’s take our Text Robot as an example. The text robot works with a deterministic data-to-text concept and refers to the automated creation of NLG texts based on a specific, structured data set and is thus not identified as AI text by Google.
The fact that data-to-text is based on the reality of the user by entering individual data ensures precision and the exclusion of false statements. Data enrichment also adds further informative aspects to the text so that the texts always offer added value for the user – one of the main criteria for Google.
You can find out more about the different technologies here.
Possible action steps
What is clearly emerging is the growing importance of unique content with added value, also known as helpful, reliable, people-first content, when it comes to placement. Information on how to create such content in the sense of Google can be found on Google itself.
However, it is not only the content alone that counts, but also the presentation on the website. This should not be impaired by disruptive elements or excessive advertising and should ensure a good user experience. In addition, content from third-party providers should be carefully checked in this context.
But what if the content has already been created with the help of AI? Given the large number of ChatGPT users – around 180.5 million – many pages have already been created with the help of AI tools, whether for support or even for the creation of entire posts. In this case, there are various options.
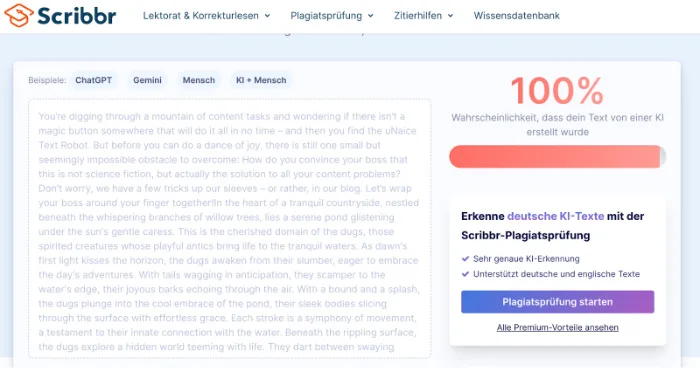
One option is the AI check: There are now a number of tools on the market that check texts to see how likely they are to have been created by an AI. Scribbr, for example, offers such a service. English texts of up to 500 characters can be tested free of charge, longer texts are subject to a fee.
Depending on the result, it is advisable to work on your texts again yourself. There are also many tools in this area that can rewrite AI texts. However, it is essential to check the revised texts again.
If you have already published a lot of empty content, it is advisable to think about reducing your content. This much is already clear – high-quality content is useful for everyone, even without the Google Core Update.
Are uNaice texts also at risk?
Have you created content with uNaice? Then don’t worry, we saw this update coming and have already taken measures to secure the content in advance. If you are still unsure, then let us clarify your questions in an appointment.
Outlook: What can we expect?
If Google achieves its announced goals, we could expect numerous penalties. But for those who have placed value on high-quality content and adhered to Google’s guidelines, there could also be new opportunities to achieve a better ranking and move past spam sites.
However, there is no guarantee – in the end it is up to Google to decide whether content is classified as spam or not. This is done using a series of parameters that cannot always be checked on a text without errors. And so we remain dependent on the goodwill of a search engine.
One thing’s for sure: This update promises to be different from previous ones, and it feels like we’ve been transported back a little to spring 2023 – everyone’s talking about AI texts.